GMO has been a hot topic for years, sparking debates at dinner tables, in classrooms, and online. With so much conflicting information swirling around, it’s no wonder many people feel unsure about what GMO foods actually are and what they mean for our health and the environment. Here are some of the most common misunderstandings about GMO foods, getting to the bottom of what’s fact and what’s fiction.
Contents
- 1 GMO Foods Are Unnatural
- 2 All GMOs Are Created in a Lab
- 3 GMOs Are Dangerous to Human Health
- 4 GMOs Cause Environmental Harm
- 5 GMOs Are Unethical and Exploit Farmers
- 6 GMOs Are Banned in Many Countries Because They Are Unsafe
- 7 Non-GMO Foods Are Always Healthier
- 8 GMOs Reduce Crop Diversity
- 9 GMOs Are Only About Big Agriculture
- 10 GMOs Are a New and Unproven Technology
- 11 GMOs Are Linked to Allergies
- 12 GMOs Are Not Labeled Because They Are Dangerous
- 13 GMOs Are Not Necessary for Food Security
- 14 GMOs Are a Silver Bullet
- 15 More From RetailShout
- 16 17 Tasty Aldi Snacks You’ll Want to Stock Up On This Month
- 17 16 Best Trader Joe’s Non-Food Products You’ll Want to Try
GMO Foods Are Unnatural
One of the most common misconceptions about genetically modified organisms (GMOs) is that they are entirely unnatural. This belief stems from the idea that humans are altering something that should be left to nature. However, almost all the food we consume has been modified over thousands of years through selective breeding and cultivation. GMOs are just a more precise method of achieving desired traits in crops, using modern science to do what farmers have done for centuries. The primary difference is the speed and accuracy with which these changes can be made.
All GMOs Are Created in a Lab

Many people believe that all GMOs are created in a sterile lab environment, completely detached from traditional agricultural practices. While it’s true that GMOs involve scientific processes, the initial development of these organisms often begins in a lab, but the cultivation of GMO crops takes place in fields just like any other plant. Moreover, the research and development process for GMOs includes extensive testing in various environments to ensure that they are safe and effective. The lab is only the beginning of a long process that eventually ends up in the soil.
GMOs Are Dangerous to Human Health

There is a pervasive fear that GMOs are harmful to human health, leading to conditions like cancer or allergies. However, extensive scientific research over the past several decades has shown that GMOs are just as safe to eat as non-GMO foods. Major health organizations, including the World Health Organization and the American Medical Association, have concluded that GMOs pose no greater risk to health than traditional crops. The rigorous testing GMOs undergo before approval ensures they meet safety standards equivalent to or even higher than non-GMO crops.
GMOs Cause Environmental Harm

Another common misunderstanding is that GMOs are inherently harmful to the environment. Critics argue that they lead to monocultures, soil degradation, and loss of biodiversity. While these are legitimate concerns in any form of agriculture, GMOs can actually be part of the solution. For instance, some GMOs are designed to be pest-resistant, reducing the need for chemical pesticides, which can harm non-target species and pollute ecosystems. Additionally, GMOs can be engineered to thrive in less-than-ideal conditions, reducing the need for land conversion and preserving natural habitats.
GMOs Are Unethical and Exploit Farmers

Many opponents of GMOs argue that they are unethical, particularly because they believe that large corporations exploit farmers by selling patented seeds that they must buy each season. While patenting is a controversial issue, it is not unique to GMOs. Many hybrid crops, which are non-GMO, are also patented. Moreover, GMOs can offer significant benefits to farmers, such as higher yields, reduced costs, and better resilience to pests and diseases. The key issue is how these technologies are used and whether fair practices are in place to protect farmers’ interests.
GMOs Are Banned in Many Countries Because They Are Unsafe

Some people believe that GMOs are banned in many countries because they are unsafe, which contributes to their negative perception. In reality, many countries that have restrictions or bans on GMOs do so due to political, economic, or cultural reasons rather than safety concerns. In fact, numerous scientific bodies around the world have endorsed the safety of GMOs. The regulatory landscape for GMOs is complex and varies from country to country, often influenced by factors other than scientific evidence alone.
Non-GMO Foods Are Always Healthier

A common assumption is that non-GMO foods are always healthier than their GMO counterparts. However, the nutritional content of a food does not depend on whether it is genetically modified. In some cases, GMOs have been developed to enhance nutritional content, such as golden rice, which is fortified with vitamin A to help combat deficiencies in developing countries. The healthiness of food depends on various factors, including how it’s grown, processed, and consumed, rather than solely on its genetic makeup.
GMOs Reduce Crop Diversity

Another misconception is that GMOs contribute to the reduction of crop diversity. Critics argue that the widespread adoption of GMOs leads to the dominance of a few varieties, pushing out traditional crops and reducing genetic diversity. While monocultures are a concern in modern agriculture, this issue is not exclusive to GMOs. In fact, GMOs can be developed to include a broader range of traits, potentially enhancing diversity within a species. The key to maintaining diversity lies in agricultural practices, including crop rotation and conservation of heirloom varieties, not in the rejection of GMOs.
GMOs Are Only About Big Agriculture

Many people associate GMOs exclusively with large agricultural corporations, believing that they are designed solely to benefit big business at the expense of small farmers. While it’s true that large companies are involved in GMO production, GMOs also offer benefits to small-scale farmers, particularly in developing countries. For instance, genetically modified crops that are drought-resistant or require fewer inputs can help small farmers increase their yields and improve food security. The narrative that GMOs are only for big agriculture overlooks the potential advantages for a wide range of farming operations.
GMOs Are a New and Unproven Technology

There is a perception that GMOs are a recent innovation and therefore unproven or risky. In reality, genetically modifying organisms is a practice that has been in development for over 30 years, with the first GMO crops introduced commercially in the mid-1990s. Since then, millions of hectares of GMO crops have been grown worldwide, and countless studies have been conducted to assess their safety and effectiveness. The technology behind GMOs is well-established, with a solid track record of benefits and safety in various agricultural applications.
GMOs Are Linked to Allergies
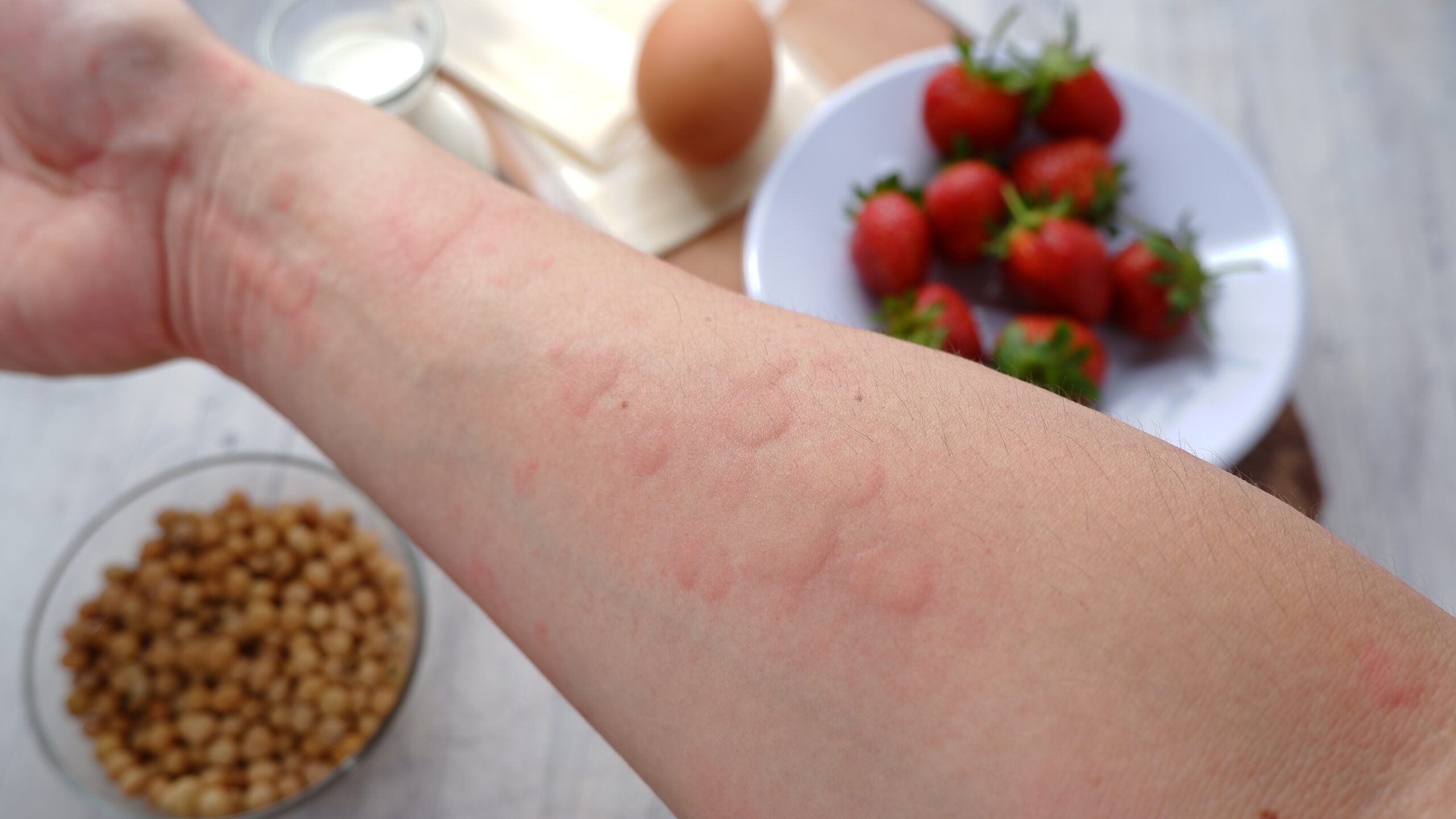

Some people believe that GMOs are more likely to cause allergic reactions than non-GMO foods. This fear is based on the idea that introducing new genes into a plant could create new allergens. However, GMOs are subject to stringent testing to ensure they do not pose any greater allergenic risk than traditional crops. Regulatory agencies require that GMOs undergo rigorous assessments, including allergenicity testing, before they are approved for the market. So far, there has been no credible evidence linking GMOs to an increase in food allergies.
GMOs Are Not Labeled Because They Are Dangerous

The lack of mandatory GMO labeling in some countries fuels the misconception that GMOs must be dangerous, otherwise, why hide them? The reality is that labeling policies are more about consumer choice than safety. In countries where GMOs are not labeled, it is not because they are unsafe but rather because the regulatory bodies have determined that GMOs are equivalent to their non-GMO counterparts in terms of safety and nutrition. In regions where labeling is required, it is often a response to consumer demand rather than a reflection of the inherent risks of GMOs.
GMOs Are Not Necessary for Food Security

Some people argue that GMOs are unnecessary for achieving global food security, believing that traditional farming methods are sufficient. However, with the growing global population and the increasing challenges posed by climate change, GMOs offer valuable tools to enhance crop resilience, increase yields, and reduce losses. For example, GMOs can be engineered to withstand extreme weather conditions, resist pests, and improve nutritional content, all of which contribute to food security. While GMOs are not the only solution, they are an important part of the broader strategy to ensure a sustainable food supply.
GMOs Are a Silver Bullet

On the flip side, there is also a misconception that GMOs are a silver bullet that will solve all agricultural problems. While GMOs offer many benefits, they are not a panacea. Successful agriculture relies on a combination of practices, including good soil management, crop rotation, pest control, and careful use of inputs. GMOs can be a powerful tool in this toolbox, but they must be used in conjunction with other methods to create a sustainable and productive agricultural system. Over-reliance on any single approach, including GMOs, can lead to unforeseen problems.
This article originally appeared on RetailShout.
More From RetailShout
16 Snacks Packed With Antioxidants for a Healthy Lifestyle

Antioxidants are essential for maintaining overall health by fighting free radicals, which can lead to oxidative stress and various chronic diseases. Incorporating antioxidant-rich snacks into your daily routine is a simple way to boost your intake of these protective compounds. Read More.
17 Tasty Aldi Snacks You’ll Want to Stock Up On This Month

Stocking up on snacks doesn’t have to mean sticking to the same old options. Aldi is the perfect place to find tasty, budget-friendly treats that are anything but boring. Read More.
16 Best Trader Joe’s Non-Food Products You’ll Want to Try

Trader Joe’s is known for its unique and affordable grocery items, but its non-food products are equally deserving of attention. From skincare essentials to eco-friendly household items, Trader Joe’s non-food lineup offers high-quality products at budget-friendly prices. Read More.






