Navigating the world of plant-based foods can sometimes feel like a scavenger hunt for hidden ingredients. While they may sound natural or harmless, some additives lurking in your favorite veggie burgers and dairy-free treats are anything but. From gut disruptors to chemical preservatives, not all plant-based ingredients are as wholesome as they seem. Here’s a breakdown of 14 sneaky ingredients to avoid if you’re aiming for a truly clean, plant-powered diet.
Contents
- 1 Carrageenan
- 2 Sodium Nitrite
- 3 Titanium Dioxide
- 4 Hexane
- 5 MSG (Monosodium Glutamate)
- 6 Soy Protein Isolate
- 7 Maltodextrin
- 8 Artificial Sweeteners (Aspartame, Sucralose)
- 9 Canola Oil
- 10 Natural Flavors
- 11 Refined Sugar
- 12 Soy Lecithin
- 13 Palm Oil
- 14 Calcium Sulfate
- 15 Sodium Aluminum Phosphate
- 16 More From RetailShout
- 17 11 Trader Joe’s Fall Home Goods You Need Before They’re Gone
- 18 19 ALDI Products You Can’t Miss This September
Carrageenan

Carrageenan is a common additive used in plant-based milks, cheeses, and other products as a thickening agent. Although it’s derived from seaweed, studies have raised concerns about its potential to cause gastrointestinal inflammation. Some evidence links carrageenan to digestive issues, such as bloating and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Inflammatory responses triggered by carrageenan can be problematic for individuals with sensitive digestive systems. It’s often recommended to check labels and opt for alternatives that do not include this additive.
Sodium Nitrite

Sodium nitrite is often used to preserve plant-based meats, particularly in sausages and deli slices. While it helps maintain the color and shelf-life of these products, sodium nitrite can form harmful compounds called nitrosamines when exposed to high heat, which are linked to an increased risk of cancer. Long-term consumption of foods with sodium nitrite may also lead to cardiovascular issues. It’s best to consume plant-based meats without this preservative or with natural alternatives like celery powder.
Titanium Dioxide

Titanium dioxide is often used to whiten plant-based products like dairy-free cheeses and vegan baked goods. While it might make your food look more appealing, it is a controversial ingredient. Some studies suggest that it may disrupt gut health by damaging the intestinal barrier, which could lead to chronic inflammation. The European Food Safety Authority has also raised concerns about its safety, recommending it be avoided in food products. Opting for plant-based foods without artificial whiteners is a safer choice.
Hexane
Hexane is a solvent used to extract oils from plants, particularly soybeans, which are a common ingredient in plant-based burgers and meat substitutes. Though most of the hexane evaporates during processing, trace amounts may remain in the final product. Prolonged exposure to hexane in high doses has been linked to neurological issues and other health risks. Choosing whole, less processed plant-based foods can help you avoid unnecessary exposure to this chemical.
MSG (Monosodium Glutamate)

Monosodium glutamate, or MSG, is a flavor enhancer commonly used in processed plant-based foods like vegan chips, snacks, and instant noodles. While the FDA considers it generally safe, some individuals report adverse reactions such as headaches, nausea, or dizziness after consuming foods with MSG. It’s also known to stimulate appetite, potentially leading to overeating. Checking labels for this additive and limiting its intake can be beneficial, especially if you are sensitive to its effects.
Soy Protein Isolate

Soy protein isolate is often found in plant-based protein powders, bars, and meat substitutes due to its high protein content. However, it is highly processed and may contain residual chemicals from the extraction process, such as hexane. Some people also report digestive discomfort or hormone disruptions due to the high levels of phytoestrogens in concentrated soy. Opting for whole soy products like tofu or edamame is a more natural and safer way to incorporate soy into your diet.
Maltodextrin
Maltodextrin, a thickening agent and sweetener, is frequently found in plant-based snacks, protein bars, and vegan sauces. It is highly processed and can spike blood sugar levels, making it problematic for those with insulin sensitivity or diabetes. Additionally, maltodextrin can feed harmful gut bacteria, potentially leading to digestive imbalances. Choosing products with natural sweeteners or without added sugars can help reduce your intake of maltodextrin.
Artificial Sweeteners (Aspartame, Sucralose)

Artificial sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose are often used in plant-based yogurts, protein shakes, and sugar-free snacks. While they may reduce calorie content, studies suggest that these sweeteners can disrupt gut health and may even lead to weight gain by altering metabolism. Some research has also linked artificial sweeteners to headaches, digestive issues, and increased cravings for sugary foods. Choosing products sweetened with natural alternatives like stevia or monk fruit is a better option.
Canola Oil

Canola oil is a common ingredient in plant-based butter, dressings, and snacks, but it is highly processed and often made from genetically modified crops. Although it’s marketed as heart-healthy, canola oil undergoes chemical extraction and refining, which can introduce harmful compounds. Some research also suggests that high consumption of omega-6 fatty acids, like those found in canola oil, can promote inflammation. Opting for healthier oils like olive or avocado oil can provide better nutritional benefits.
Natural Flavors

The term “natural flavors” on plant-based food labels can be misleading, as it may include chemically processed ingredients derived from plants or animals. While they are used to enhance taste, the exact composition of natural flavors is often unknown, which raises concerns for individuals with allergies or sensitivities. Additionally, the processing methods can diminish any potential health benefits the original source might have offered. It’s best to look for products that clearly state the origin of their flavors.
Refined Sugar

Refined sugar is frequently added to plant-based desserts, yogurts, and beverages to improve taste. However, consuming too much refined sugar can lead to blood sugar spikes, weight gain, and increased risk of chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease. Many refined sugars are processed using bone char, making them unsuitable for strict vegans. Opt for products sweetened with natural alternatives like maple syrup, coconut sugar, or agave nectar to avoid these risks.
Soy Lecithin

Soy lecithin is commonly used as an emulsifier in plant-based chocolates, protein powders, and dairy-free creams. While it’s generally considered safe, soy lecithin is often derived from genetically modified soybeans and may contain pesticide residues. Some people with soy allergies or sensitivities may also experience adverse reactions when consuming products with soy lecithin. Choosing products with alternative emulsifiers or organic versions can help avoid potential health concerns.
Palm Oil
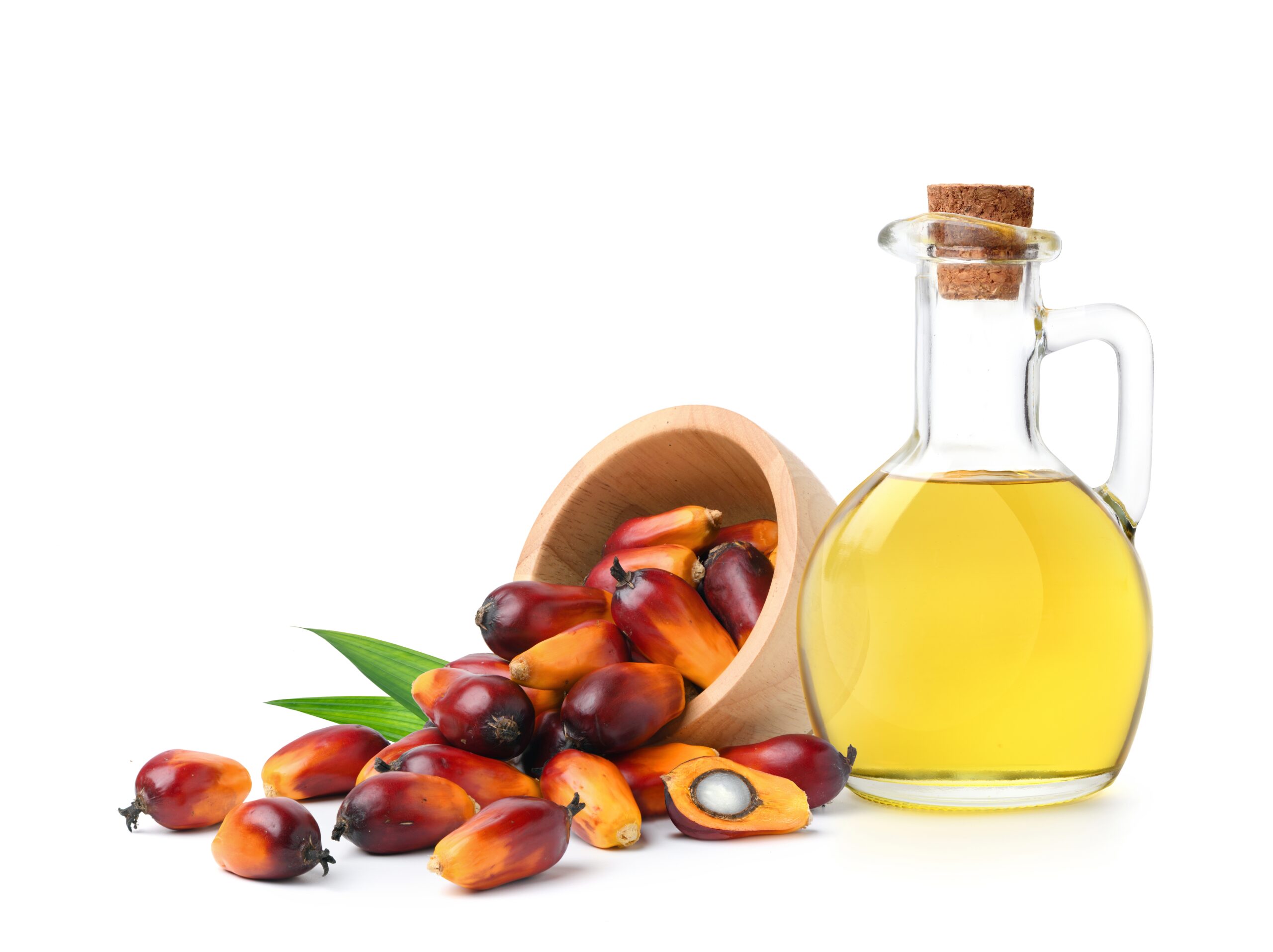

Palm oil is a frequent ingredient in plant-based margarine, snacks, and frozen foods. While it’s a plant-derived fat, palm oil is highly controversial due to its environmental impact and potential health risks. It is high in saturated fat, which can contribute to heart disease if consumed in large amounts. Additionally, the production of palm oil has led to widespread deforestation and habitat destruction. Choosing products that use sustainably sourced palm oil or other fats like coconut oil can be a more ethical choice.
Calcium Sulfate

Calcium sulfate is used as a firming agent in plant-based tofu, bread, and other processed foods. Although it’s considered safe in small amounts, overconsumption of calcium sulfate can cause digestive discomfort or constipation. Additionally, its presence in highly processed foods means you might be consuming more than intended. Opting for less processed alternatives or carefully monitoring the quantity in your diet can help prevent potential side effects.
Sodium Aluminum Phosphate

Sodium aluminum phosphate is often used in plant-based baking mixes and processed foods to help them rise. While it enhances texture, excessive consumption of aluminum-based additives may pose health risks, including neurological conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. It can also interfere with calcium absorption, which is essential for bone health. Choosing baked goods that use non-aluminum leavening agents is a better option for long-term health.
This article originally appeared on RetailShout.
More From RetailShout
15 Immune-Boosting Foods You Should Eat Regularly

Staying healthy is more than just washing your hands and getting enough sleep—it starts with what’s on your plate. A strong immune system starts with the right fuel, and certain foods pack a punch when it comes to supporting your immune system. Read More.
11 Trader Joe’s Fall Home Goods You Need Before They’re Gone

Fall has officially taken over at Trader Joe’s, and their seasonal home goods are flying off the shelves faster than you can say “pumpkin spice.” From cozy candles to autumn-inspired kitchen essentials, TJ’s is stocking some quirky and fun home goods to bring those fall vibes into your home. Read More.
19 ALDI Products You Can’t Miss This September

September at ALDI is always full of surprises, and this year is no different. They’re rolling out all kinds of goodies, from festive pastas to fall-inspired desserts that you won’t want to miss. Read More.






