Cooking at home can be a delightful experience, especially when you have the right techniques up your sleeve. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to up your game in the kitchen, mastering a few essential cooking techniques can make a world of difference. These techniques will not only improve the taste and presentation of your dishes but also make cooking more enjoyable and efficient.
Contents
- 1 Knife Skills
- 2 Mise en Place
- 3 Searing
- 4 Sauteing
- 5 Roasting
- 6 Braising
- 7 Poaching
- 8 Blanching
- 9 Grilling
- 10 Baking
- 11 Boiling
- 12 Simmering
- 13 Stewing
- 14 Steaming
- 15 Frying
- 16 Broiling
- 17 Blending
- 18 Caramelizing
- 19 Deglazing
- 20 Marinating
- 21 Food Preservation
- 22 Plating
- 23 More From RetailShout
- 24 15 Italian Recipes That Are Actually Super Simple To Make
- 25 10 Remarkable Origin Stories Behind Popular Foods
Knife Skills
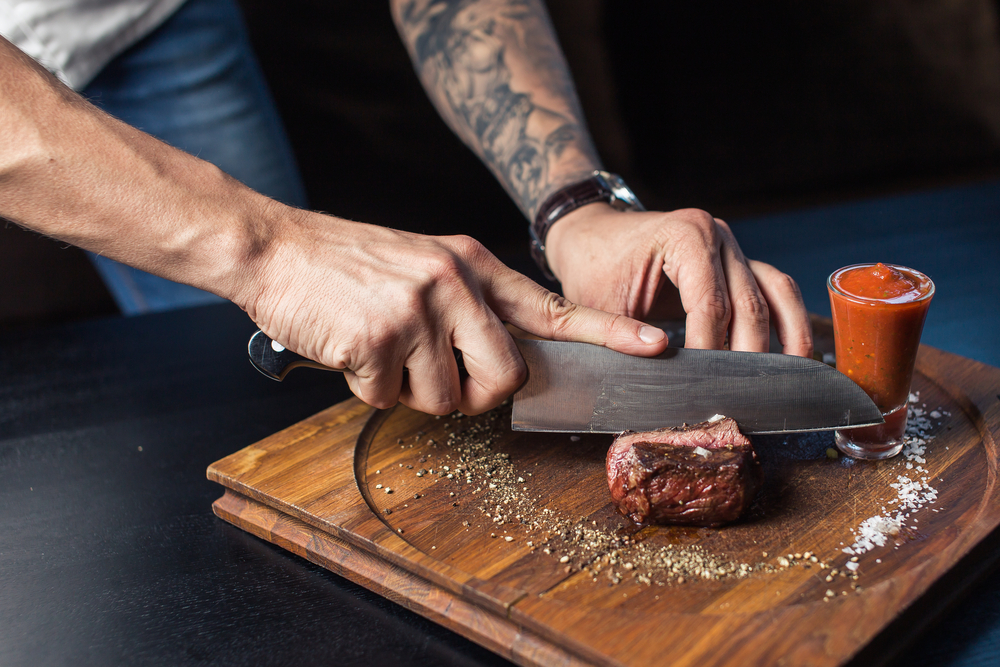

Mastering knife skills is the foundation of efficient and safe cooking. Learn to hold the knife correctly, use a rocking motion, and practice basic cuts such as dicing, slicing, and julienning. Regularly sharpen your knives to maintain precision and reduce the risk of accidents. Proper knife skills improve the texture and presentation of your dishes. Start with softer vegetables and gradually move to harder ones as you gain confidence.
Mise en Place
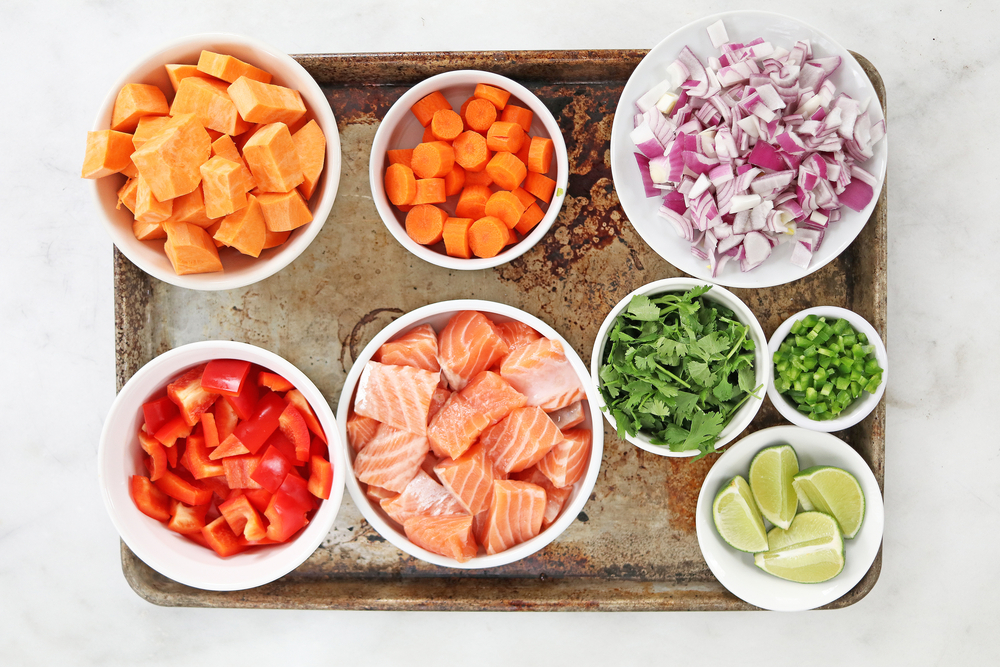

Mise en place, meaning “everything in its place,” involves preparing and organizing ingredients before cooking. This technique ensures a smooth cooking process and reduces stress. Chop, measure, and set out all ingredients before you start cooking. It improves efficiency and helps prevent mistakes
Searing
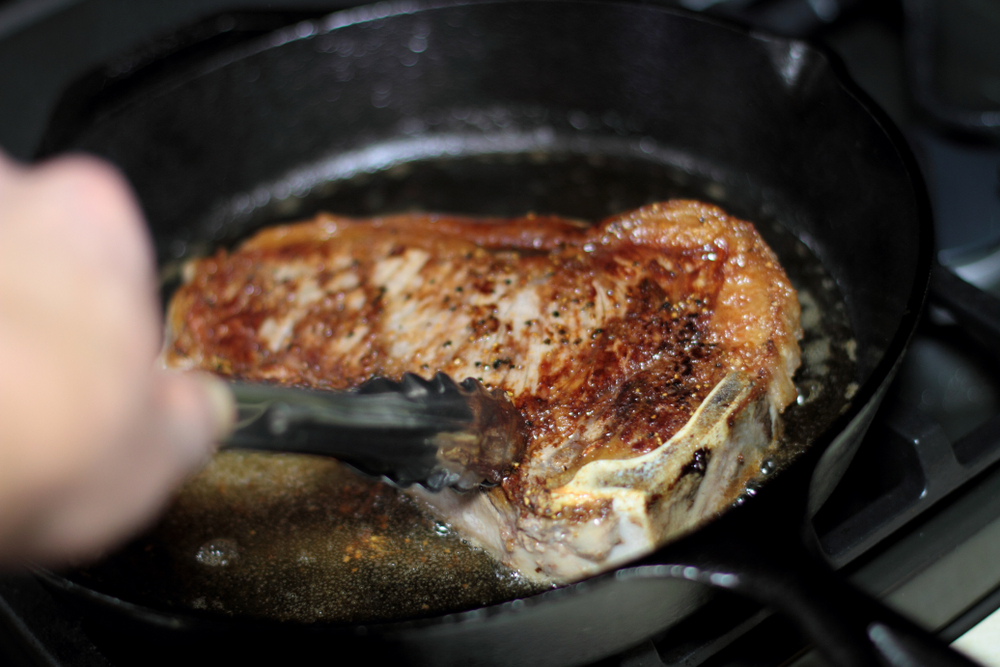

Searing involves cooking the surface of food at high temperatures until a brown crust forms. Use a heavy pan like cast iron, preheat it until it’s smoking hot, and avoid overcrowding the pan to ensure a perfect sear. This technique enhances the flavor and texture of meats and vegetables by creating a caramelized crust. It’s crucial for dishes like steaks, where a quick, intense heat locks in juices and flavors.
Sauteing
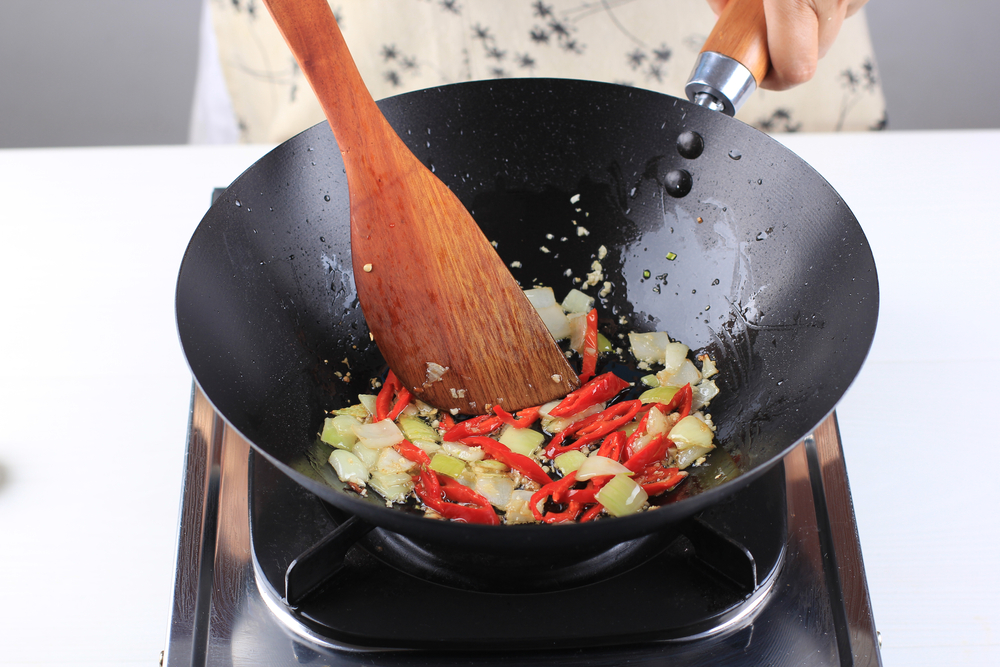

Sautéing is a method of cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil or butter over medium-high heat. Cut ingredients into uniform pieces to ensure even cooking and stir frequently to prevent burning. This technique is ideal for vegetables, meats, and seafood, allowing you to cook them quickly while preserving their texture and flavor. Use a large skillet to give ingredients enough space to cook evenly.
Roasting
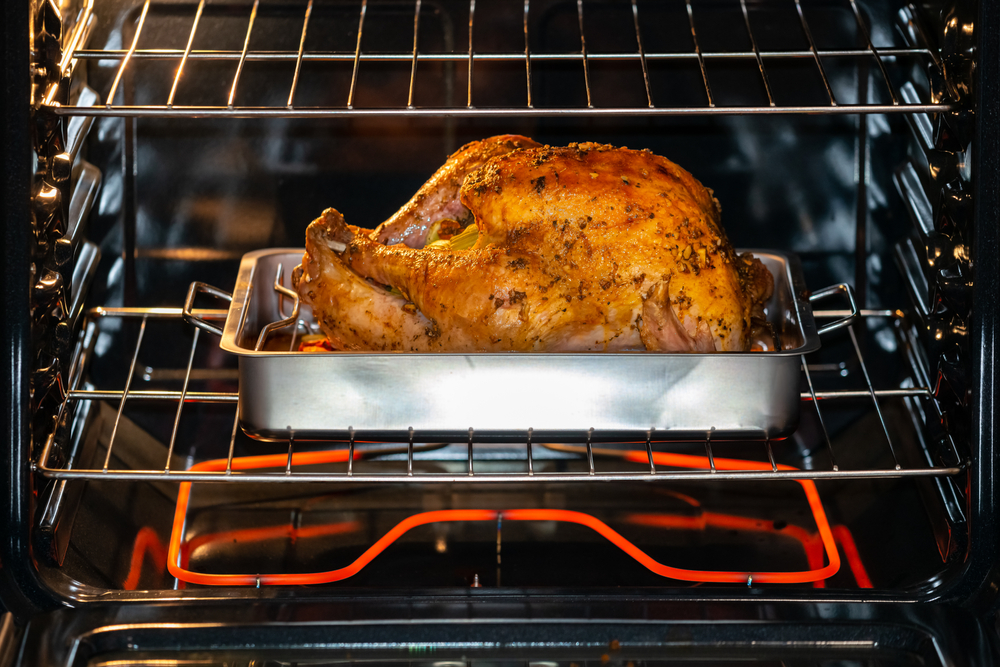

Roasting involves cooking food in an oven using dry heat, which evenly surrounds the food to cook it on all sides. Preheat the oven to the desired temperature, and place the food on a rack or a baking sheet. Roasting is perfect for meats and vegetables, developing deep flavors and a caramelized exterior. Experiment with different seasonings and oils to enhance the taste.
Braising
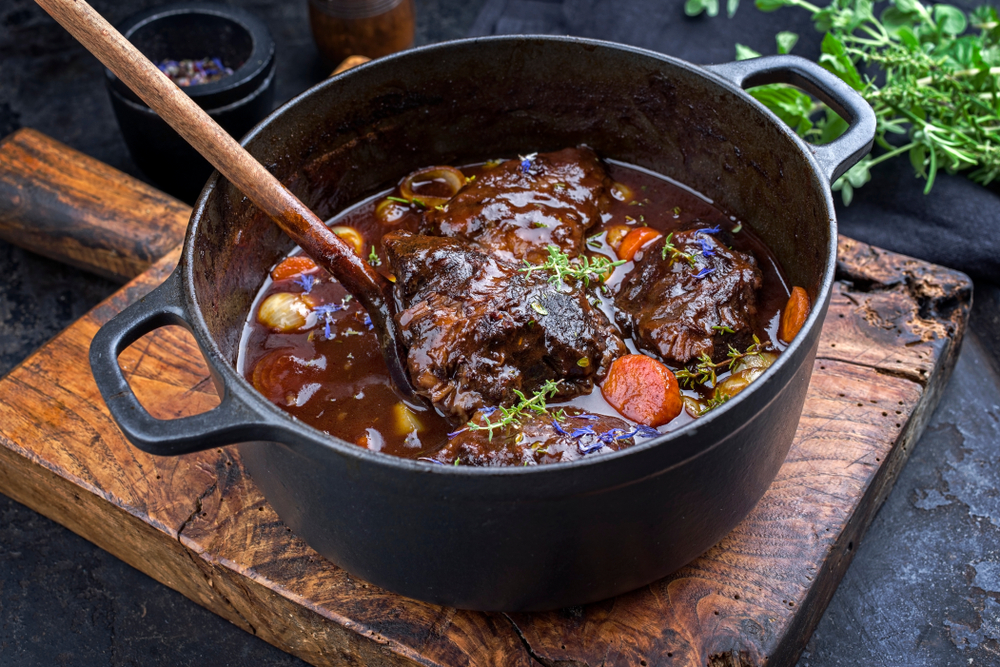

Braising is a slow-cooking method that combines both wet and dry heats. First, sear the food at high temperatures, then cook it slowly in a covered pot with some liquid. This technique is great for tough cuts of meat, as the slow cooking process breaks down the connective tissues, making them tender and flavorful. Use a heavy pot with a tight-fitting lid to retain moisture.
Poaching
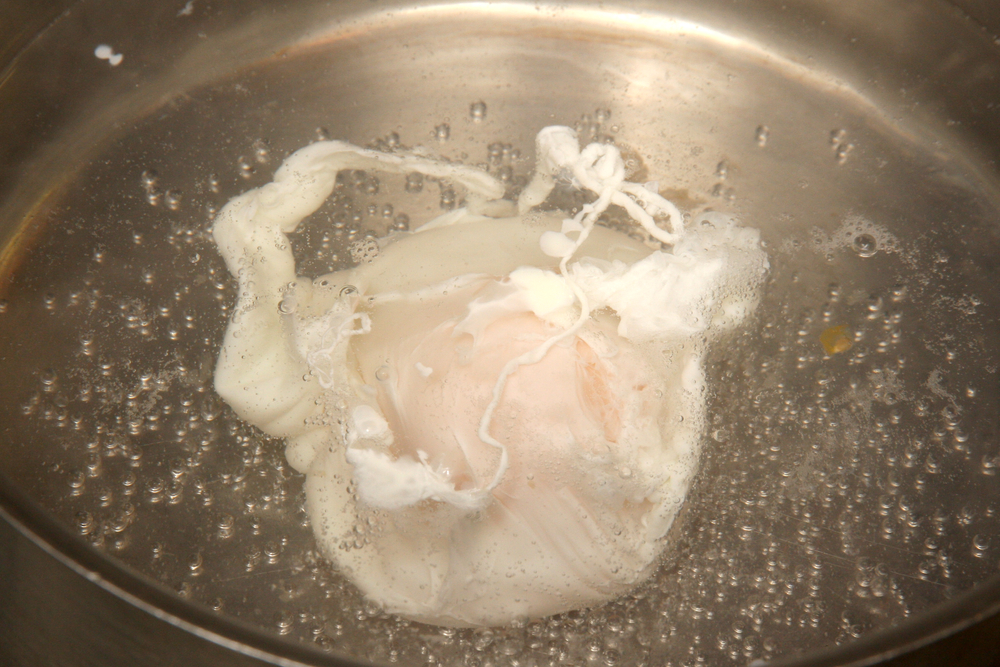
Poaching involves cooking food in a liquid at a low temperature, typically between 160°F and 180°F. It’s a gentle cooking method suitable for delicate items like fish, eggs, and fruit. Keep the liquid just below simmering to ensure the food cooks evenly without becoming tough. Add aromatics like herbs and spices to the poaching liquid to infuse flavor.
Blanching
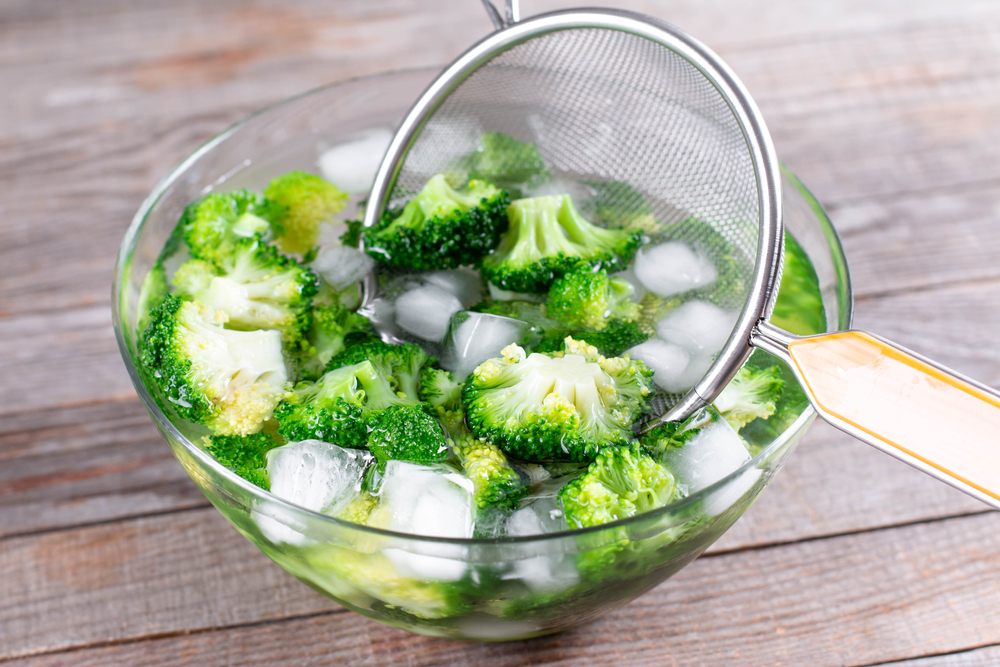

Blanching is a two-step process where food is briefly cooked in boiling water and then quickly submerged in ice water. This technique is used to soften vegetables, remove skins, and preserve vibrant colors. It also helps to prepare vegetables for freezing. After blanching, drain the food well before using it in your recipes.
Grilling
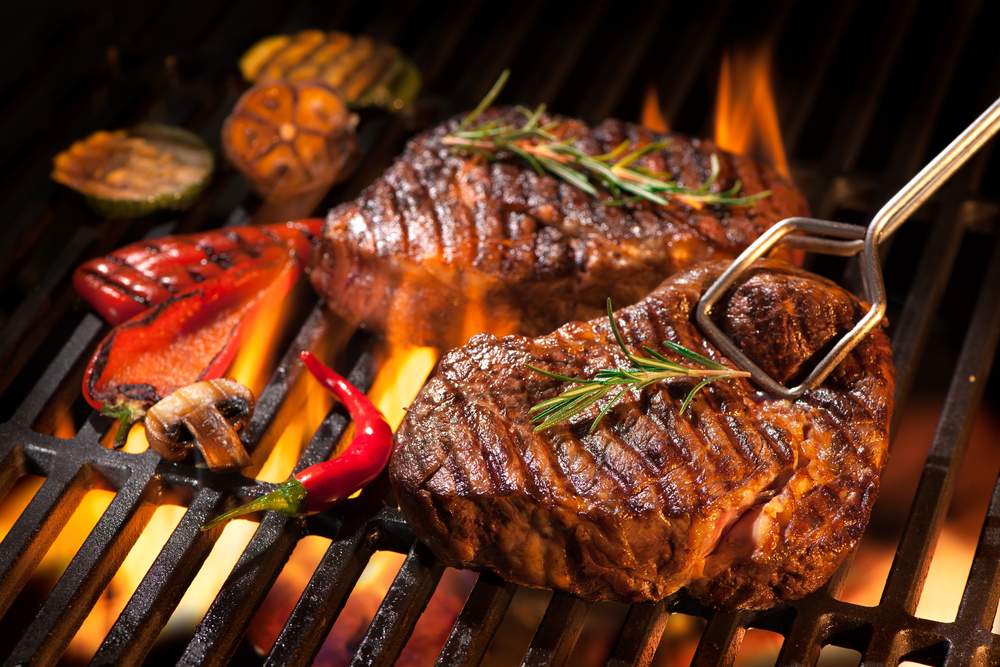

Grilling involves cooking food over direct heat, typically on a grill or barbecue. Preheat the grill to ensure it’s hot enough to sear the food quickly, locking in juices. Grilling adds a smoky flavor and is perfect for meats, vegetables, and even fruits. Use marinades and rubs to enhance the taste, and turn the food only once to achieve the best grill marks.
Baking
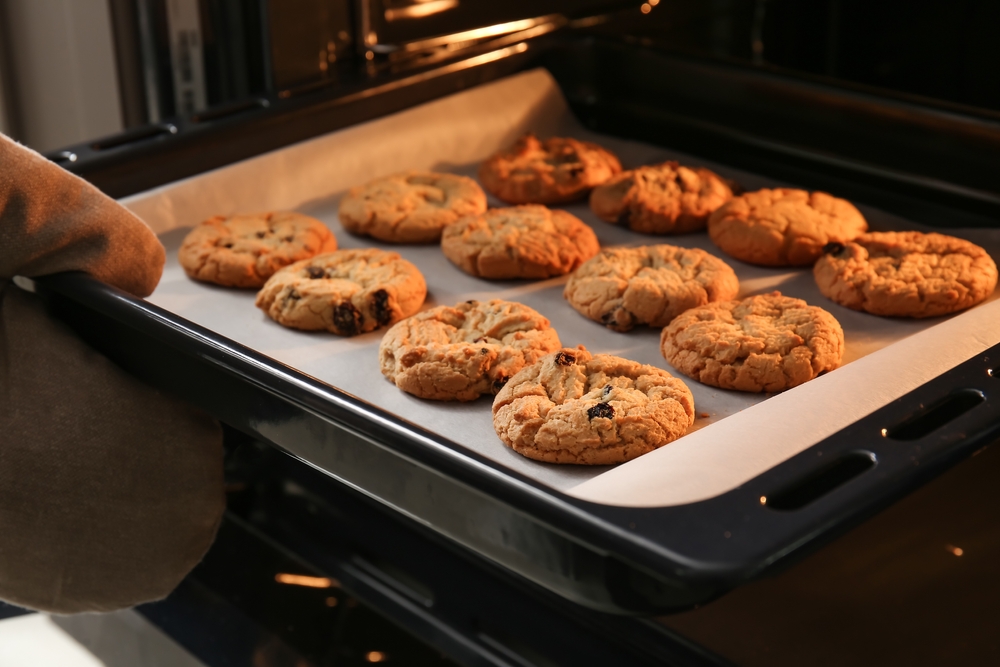

Baking uses prolonged dry heat, typically in an oven, to cook food. It’s essential for making bread, cakes, pastries, and casseroles. Preheat the oven to the correct temperature and follow recipes carefully to achieve consistent results. Use an oven thermometer to ensure accuracy and avoid opening the oven door frequently, which can cause temperature fluctuations.
Boiling
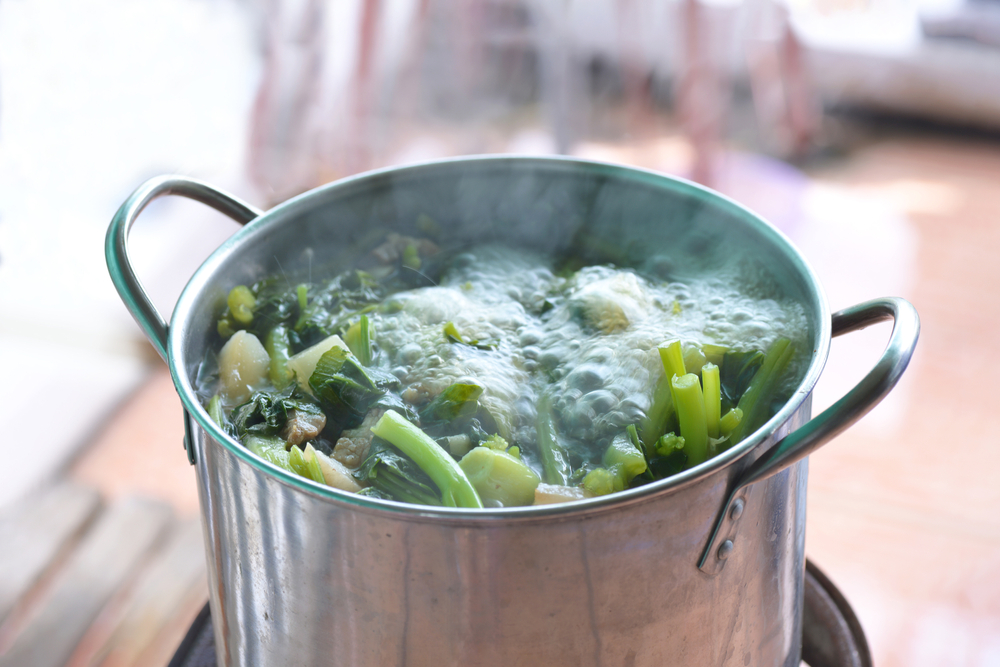

Boiling involves cooking food in water or broth at 212°F. It’s a fast method suitable for pasta, grains, and hard vegetables. Ensure you use a large pot with plenty of water to allow the food to move freely and cook evenly. Season the water with salt to enhance the flavor of the food.
Simmering
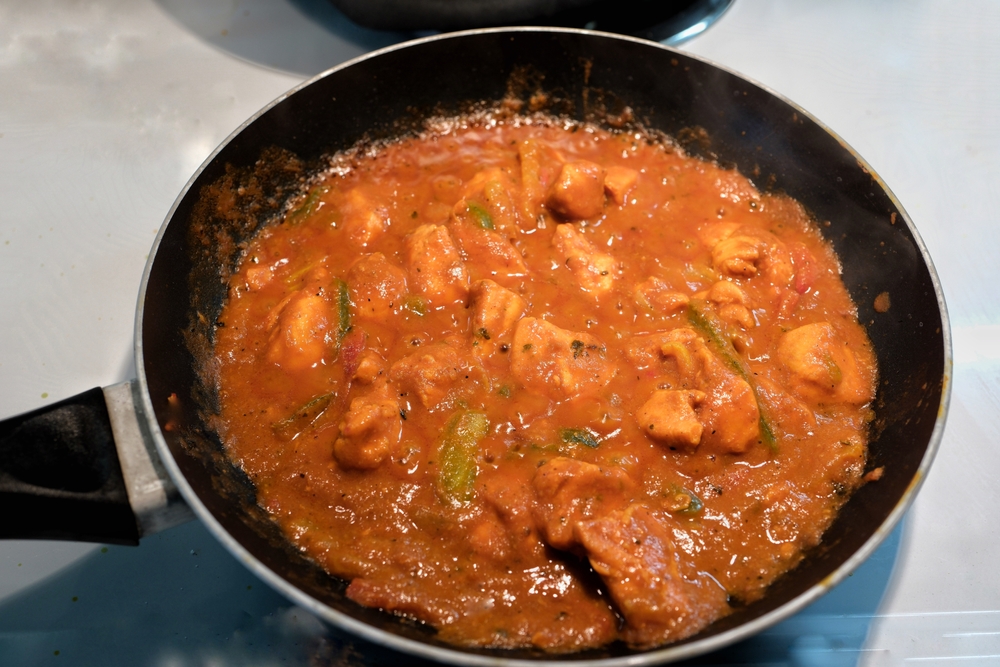

Simmering is a cooking method where food is cooked in liquid at a temperature just below boiling, usually between 185°F and 205°F. It’s ideal for soups, stews, and sauces, allowing flavors to meld and develop slowly. Keep the heat low and avoid vigorous boiling to prevent toughening of meats and overcooking of vegetables.
Stewing
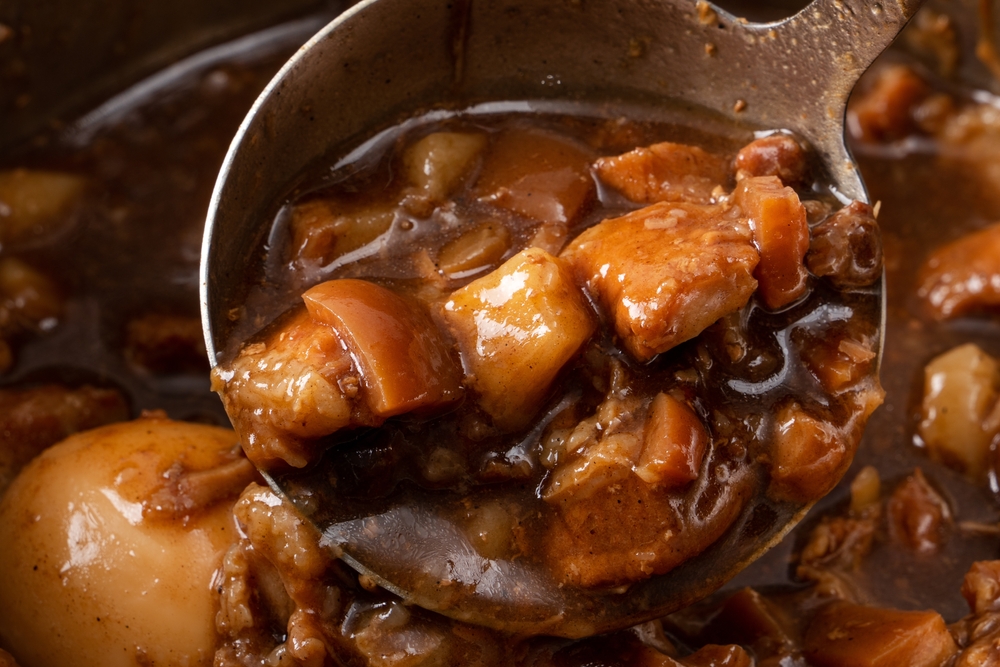

Stewing is a slow-cooking method that involves cooking food in liquid at a low temperature for an extended period. It’s perfect for tough cuts of meat and root vegetables, as the slow cooking process tenderizes them and blends the flavors. Use a heavy pot with a tight-fitting lid to retain moisture and stir occasionally to prevent sticking.
Steaming
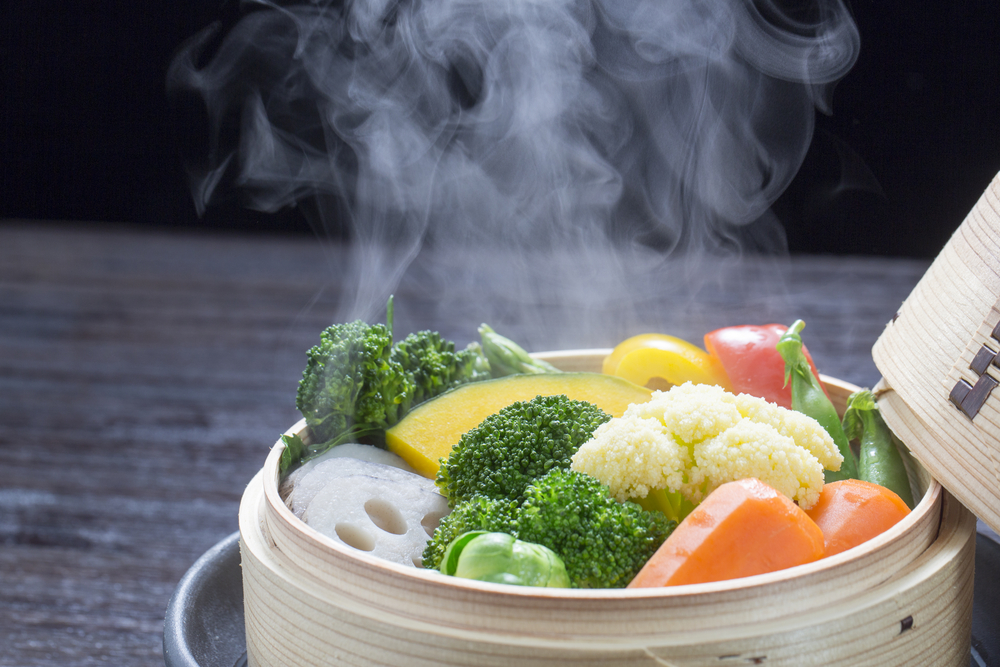

Steaming is a gentle cooking method that uses steam to cook food without immersing it in water. It’s ideal for preserving nutrients and the natural flavors of vegetables, fish, and dumplings. Use a steaming basket or a colander over boiling water, and cover the pot to trap the steam. Ensure that the water level is below the basket to prevent the food from becoming soggy.
Frying
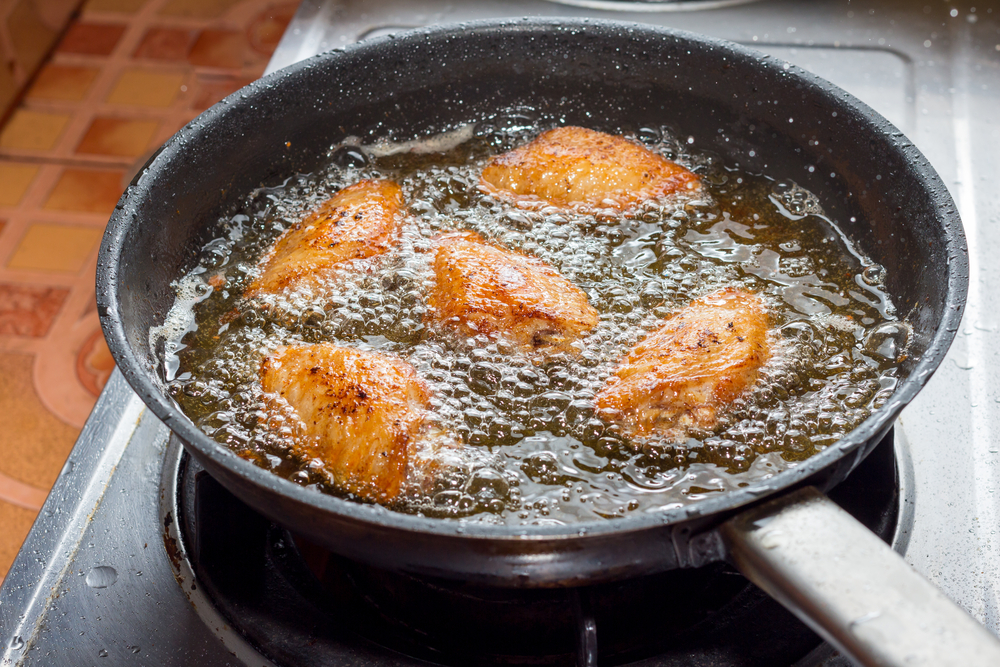

Frying involves cooking food in hot oil or fat, which creates a crispy exterior while keeping the interior moist. There are different frying methods, such as deep-frying, shallow-frying, and stir-frying. Maintain the oil at the correct temperature to avoid greasy food and use a slotted spoon or tongs to handle the food safely. Drain fried food on paper towels to remove excess oil.
Broiling
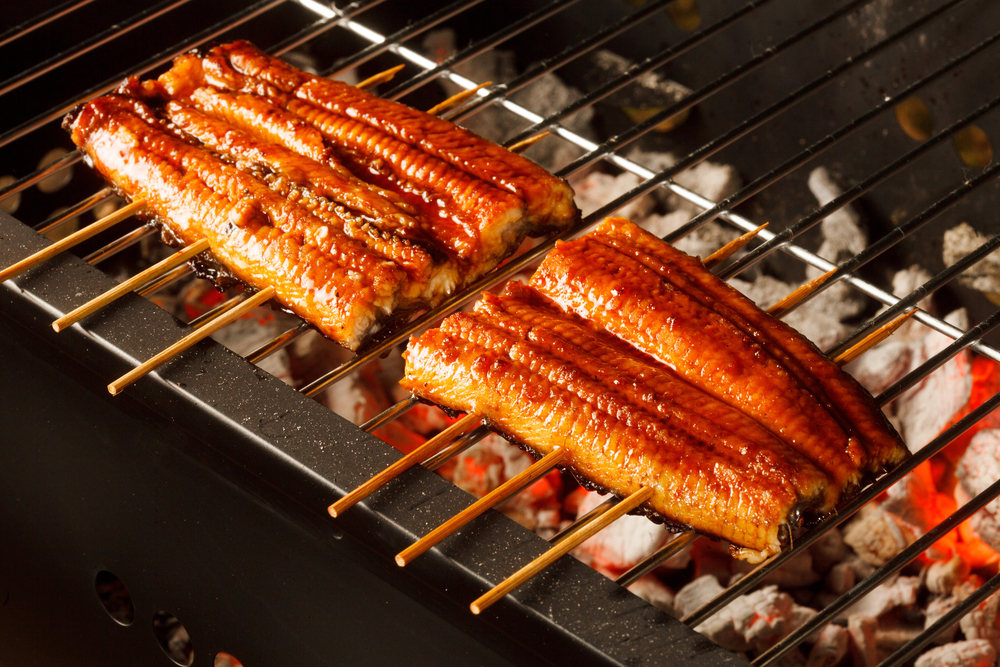

Broiling uses high, direct heat from above to cook food quickly. Preheat the broiler, place food on a broiler pan, and position it close to the heat source. Turn the food halfway through cooking for even browning. Broiling is perfect for thin cuts of meat, fish, and vegetables, creating a charred, caramelized surface.
Blending
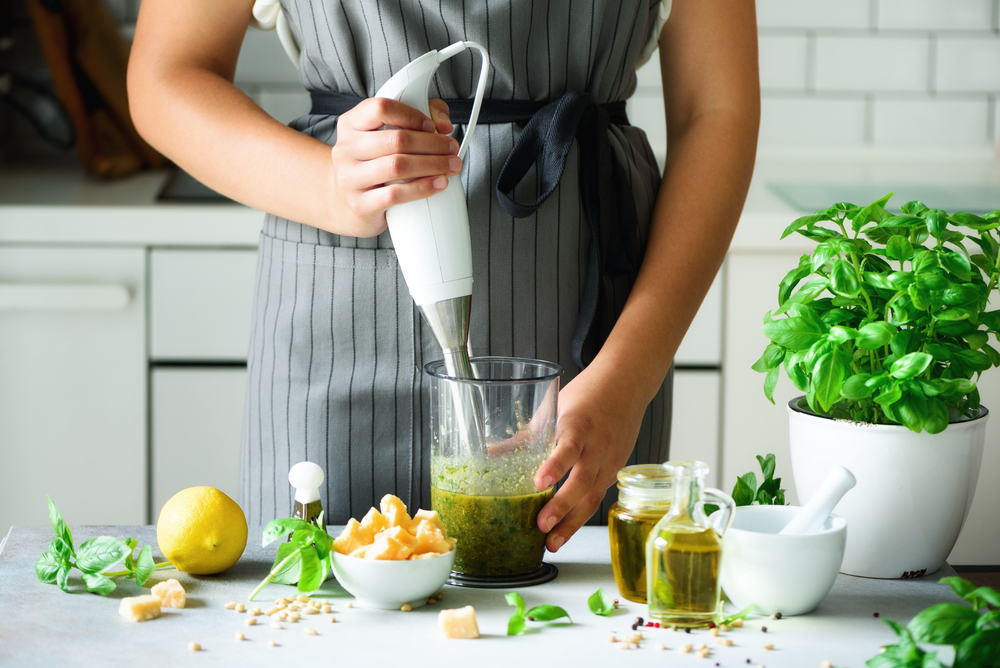

Blending mixes ingredients into a smooth, uniform consistency using a blender or food processor. This technique is essential for making soups, sauces, smoothies, and purees. Start with soft ingredients and add liquids gradually for smoother results. Blending can also emulsify mixtures, such as in making mayonnaise or salad dressings.
Caramelizing
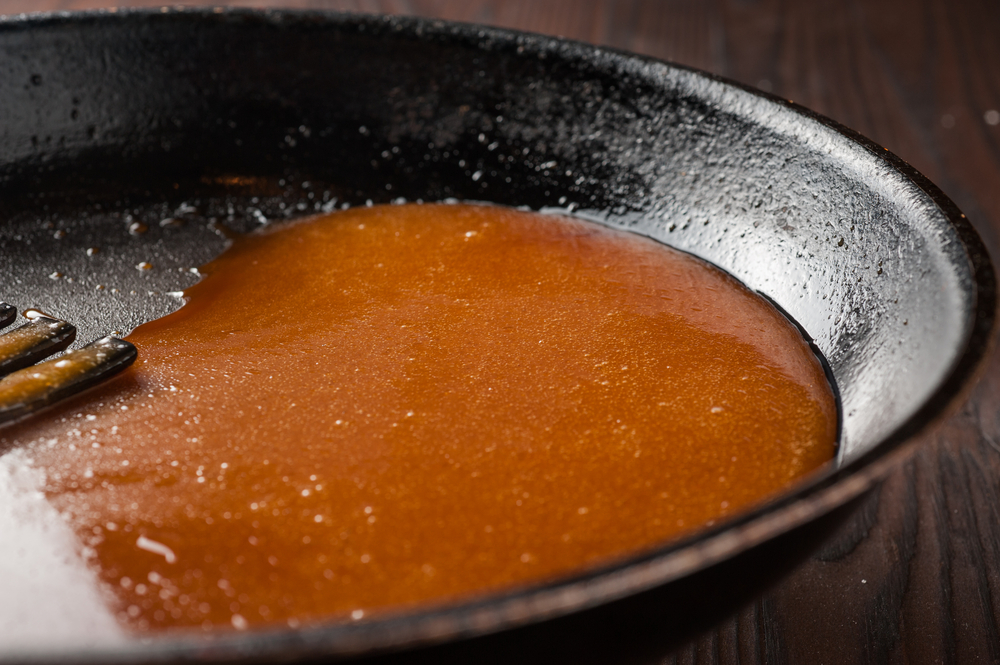

Caramelizing involves cooking sugar until it turns into a golden brown syrup. Use a heavy-bottomed pan to ensure even heat distribution. Stir constantly to prevent burning and achieve the desired color and flavor. Caramelizing adds depth and sweetness to dishes, enhancing items like onions, desserts, and sauces.
Deglazing
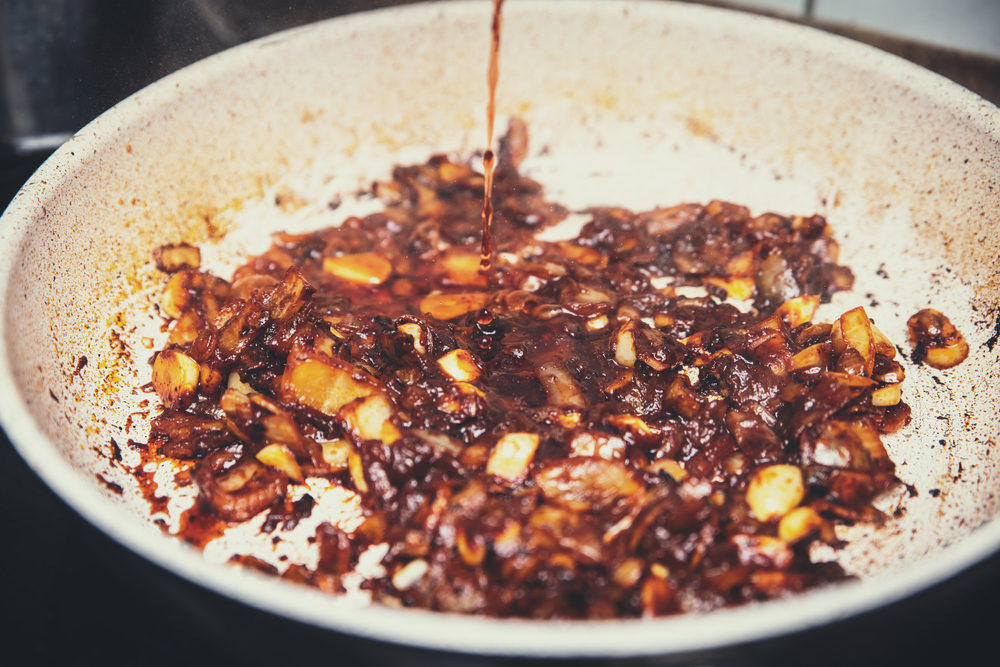

Deglazing involves adding liquid to a hot pan to dissolve browned food particles stuck to the bottom. This technique creates a flavorful base for sauces and gravies. Use wine, broth, or vinegar as the deglazing liquid and scrape the pan with a wooden spoon to incorporate the fond into the sauce. Allow the liquid to reduce and concentrate the flavors before serving.
Marinating
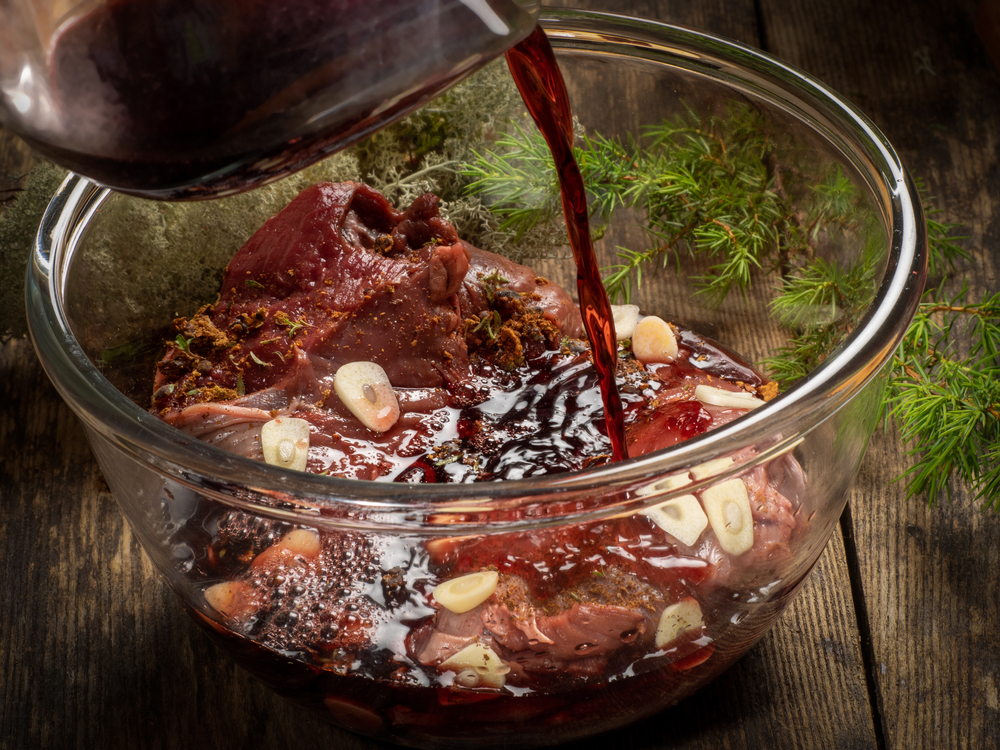

Marinating involves soaking food in a seasoned liquid to add flavor and tenderize it. Use acidic ingredients like vinegar, citrus juice, or yogurt to break down proteins in meats, making them more tender. Marinate in the refrigerator for safety, and discard the marinade used on raw food to avoid contamination. Experiment with different herbs, spices, and liquids to create unique flavor profiles.
Food Preservation
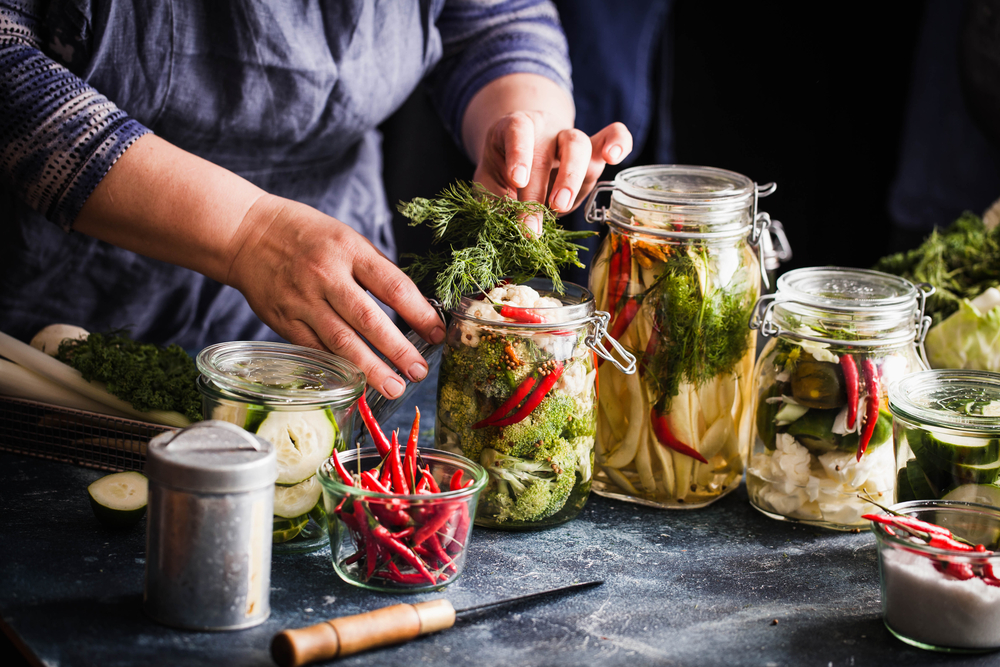

Food preservation techniques like pickling and canning extend the shelf life of seasonal ingredients. These methods allow you to enjoy fruits and vegetables year-round. Follow proper procedures to ensure food safety and quality. Properly preserved foods can be used in various recipes and as standalone snacks
Plating
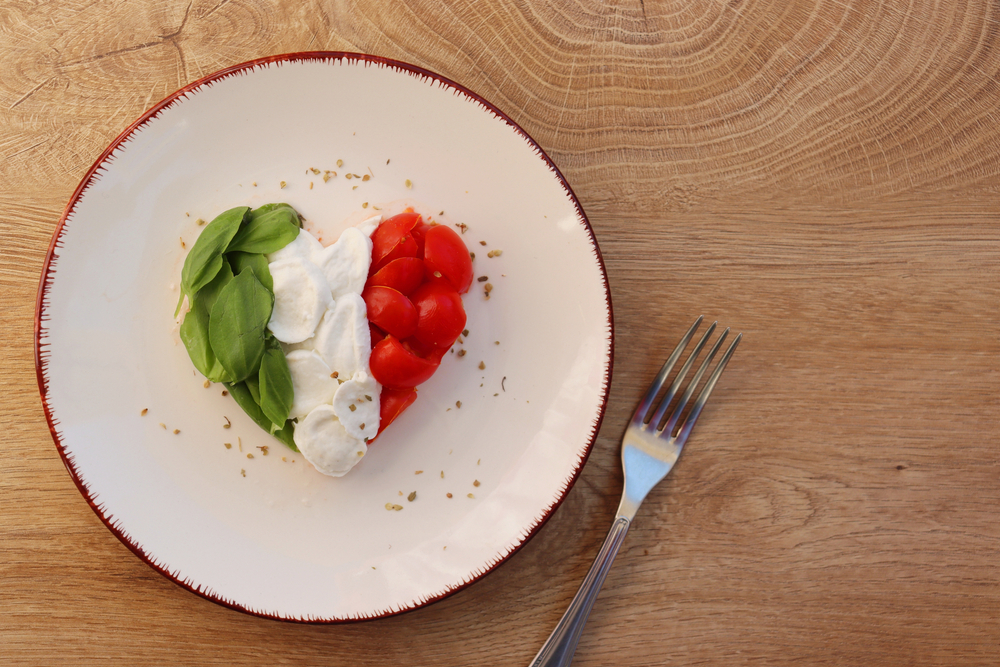

Plating is the art of arranging food on the plate in an appealing way. Consider color, texture, and arrangement to create a visually attractive dish. Use garnishes, sauces, and edible flowers to add final touches. Plating enhances the dining experience by making the food look as good as it tastes, impressing guests and elevating home-cooked meals.
This article originally appeared on RetailShout
More From RetailShout
26 Cooking Projects That Make Learning Fun for Kids

Cooking with kids is an awesome way to have fun and learn new skills together. It’s not just about making delicious food; it’s also about teaching important lessons in a hands-on way. Imagine the joy on your child’s face as they mix, measure, and create something tasty from scratch. Read More.
15 Italian Recipes That Are Actually Super Simple To Make

Craving the rich and comforting flavors of Italy but short on time? Whether you’re a novice in the kitchen or a seasoned home cook, these dishes will bring the essence of Italian cuisine right to your table with minimal effort. Read More.
10 Remarkable Origin Stories Behind Popular Foods

Imagine biting into a slice of pizza or savoring a scoop of ice cream and wondering where these delicious treats came from. Well, every dish has a story, and some of your favorite foods have origins that are as interesting as their flavors. Read More.






